European Patent Office Prior Art Nonpatent Literature Submission Date
This is a list of legal terms relating to patents. A patent is not a right to practise or utilize the invention, simply a territorial correct to exclude others from commercially exploiting the invention, granted to an inventor or his successor in rights in commutation to a public disclosure of the invention.
A [edit]
Abandonment [edit]
The reply of an bidder to an office activity must exist made within a prescribed time limit. If no reply is received within the time period, the application may be considered, depending on the jurisdiction, as abandoned or deemed to be withdrawn, and, therefore, no longer pending.
Allowance [edit]
A patent is "immune" when the patent office examiners have determined that the patent application meets the necessary criteria of novelty, non-obviousness, feasibility, and usefulness. The applicants are notified of this certification, and that the patent office is ready to grant the patent once certain fees are paid and paperwork filed by the inventors or assignees. The term is used in the U.South. and some other countries. Few allowed patents are not subsequently granted.
Annuity fee [edit]
A fee to be paid to maintain a patent or a patent awarding in force. Also called "maintenance fee" or "renewal fee".
Awarding [edit]
An application for a patent, or patent awarding, is a request by a person or visitor to the competent potency (ordinarily a patent office) to grant him a patent. By extension, a patent application likewise refers to the content of the document which that person or visitor filed to initiate the application procedure. This document commonly contains a clarification of the invention and at least i claim used to define the sought scope of protection.
Assignor estoppel [edit]
In United States patent law, an equitable estoppel barring a patent'southward seller (assignor) from attacking the patent's validity if he/she is establish to accept infringed that patent afterwards.
Auslegeschrift [edit]
In outdated German patent police force, the second reading, or publication, of a patent application.
[edit]
A form of inventor'south recognition formerly available in the Soviet Matrimony[1] and a number of Socialist countries.[2] As well called "inventor's certificate".[ii]
B [edit]
Biogen sufficiency [edit]
U.K. law concept according to which, if "the extent of the monopoly claimed [in a patent] exceeds the technical contribution to the art made by the invention as described in the specification", the patent may be revoked on the ground of insufficiency of disclosure. The concept stems from the decision Biogen v. Medeva, issued by the Business firm of Lords on 31 October 1996.[iii]
Bolar exemption [edit]
Meet inquiry exemption.
Branching off [edit]
Under German patent law, a procedure consisting in deriving a utility model (High german: Gebrauchsmuster) from a awaiting patent application. Likewise chosen "derivation".[4] [5] The corresponding German term is Abzweigung.
C [edit]
Catch and release [edit]
The practice of a patent holding visitor ownership a patent, offering a license to its members and so selling or donating the patent after a sure menstruum of time.[6]
Chapter I [edit]
In the Patent Cooperation Treaty (Per centum), "Chapter I" refers to the prosecution process when no need under Article 31 Per centum is fabricated. Us selected under Affiliate I past the bidder are called "designated States".[7]
Chapter 2 [edit]
In the PCT, "Chapter II" refers to the prosecution process when a need under Article 31 Per centum is fabricated. An international preliminary examination is conducted in this case. The demand indicates the Contracting State or States in which the applicant intends to apply the results of the international preliminary examination ("elected States").[eight]
Claim [edit]
A noun phrase defining the extent of the protection conferred by a patent, or the extent of protection sought in a patent awarding.
Claim chart [edit]
A chart often used in the context of patent litigation for analyzing and presenting information regarding a patent claim vis-à-vis an allegedly infringing product or method.
Claim structure [edit]
The process of interpreting or explaining the meaning of the terms in a patent claim, particularly in the context of patent infringement.
Clearance search and opinion [edit]
A search done on issued patents or on pending patent applications to determine if a product or procedure infringes whatsoever of the claims of the issued patents or pending patent applications. These searches and opinions are also called liberty-to-operate searches and opinions. Meet Patent infringement.
Mutual general noesis [edit]
A legal concept used notably when assessing whether an invention involves an inventive step, whether the disclosure of the invention is sufficiently clear and complete for a skilled person in the fine art to be able to carry out the invention, and whether the subject-matter of a prior art disclosure is enabling.[nine] The common general cognition "is the common knowledge in the field to which the invention relates." The information "must exist more often than not known and generally regarded as a skilful ground for farther activeness by the bulk of those engaged in that art before it becomes office of their common stock of cognition relating to the art, and and then function of the mutual general cognition."[10]
Regarding the inventive footstep cess, "[if] information is part of the common general knowledge and so information technology forms part of the stock of knowledge which will inform and guide the skilled person's approach to the problem from the showtime. Information technology may, for case, affect the steps it volition exist obvious for him to take, including the nature and extent of any literature search."[11]
Nether European exercise, "the mutual general knowledge of the person skilled in the fine art is, every bit a general rule, established on the basis of encyclopaedias, textbooks and the like".[12] Exceptionally withal, common general cognition may also exist established on the footing of the content of patent specifications "and in particular when a serial of patent specifications provides a consistent movie that a particular technical procedure was generally known and belonged to the common general knowledge in the art at the relevant engagement".[13]
Compulsory license [edit]
Using compulsory licenses, a authorities may force a patent proprietor to grant utilize to the state or others. Normally, the holder does receive some royalties, either set by law or adamant through some form of arbitration.
Continuation-in-function application [edit]
Under United States law, a type of continuing application in which the applicant adds subject-thing not disclosed in the parent awarding, but repeats substantial portion of the parent'due south specification, and shares at least i inventor with the parent application. See continuing patent application.
Continuing application [edit]
In United states of america law, an active patent application, prior to final action, may give rising to additional applications for additional claims carrying the priority engagement of the original awarding. With the move to published applications, this has get a common way of producing submarine patents.[14]
Contribution approach [edit]
Under European patent practice, a legal approach, now abandoned by the European Patent Function (EPO), for assessing whether an invention was patentable. The approach consisted in establishing whether the "contribution to the art" made by the invention was only in a field excluded from patentability by Article 52(2) and (3) EPC and, if and then, the application could be refused.[15] The EPO now applies the sometimes named "any hardware" or "whatsoever technical means" arroyo, notably formulated in EPO Board of Appeal decisions T 258/03 (Auction Method/Hitachi) and T 424/03 (Microsoft).[xvi]
Contributory infringement [edit]
A form of indirect infringement.
D [edit]
DAS (Digital Access Service) [edit]
A system for exchanging priority documents electronically.[17] [xviii] Too referred to equally "WIPO DAS".
Annunciation of not-infringement [edit]
A declaration obtained from a court that one'due south actions exercise not infringe a detail patent. An action for a declaration of non-infringement may be brought before a courtroom every bit a preventive measure prior to beingness sued past a patent proprietor, for example if an infringement arrange is believed to be imminent.
Defensive patenting [edit]
A practice consisting in "obtaining patents to stake [one's] claim to an area of technology in hopes of preventing other companies from suing them."[19] See also defensive patent aggregation.
Defensive publication [edit]
A publication intended to foreclose the grant of a patent to a competitor by placing information in the public domain.
Defensive termination [edit]
An implicit cantankerous license where the licensor tin terminate a patent license if the licensee turns around and sues the licensor for infringing a patent.
Demand letter [edit]
A letter of the alphabet sent to a company "seeking royalties and threatening legal action for patent infringement."[twenty] Likewise called a "threat letter of the alphabet".
Need under Chapter Ii [edit]
A request to bailiwick an international application to an international preliminary examination under Chapter II of the Patent Cooperation Treaty (Percentage).[21]
Dependent claim [edit]
A claim comprising all the features of another merits.[22]
Pattern around [edit]
The act of developing an alternative appliance or method (which may in itself also be a patentable invention), that does non borrow upon an issued patent. Also used equally a noun.
Designated office [edit]
Under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (Percentage), a national patent office of or acting for a Land designated by the applicant under Affiliate I of the PCT.[23] See also "Chapter I" higher up.
Disclaimer [edit]
In a merits, words identifying subject-matter that is not claimed[24] or, past extension, an amendment consisting in limiting a claim past introducing therein a negative technical characteristic.[25]
Divided infringement [edit]
In U.S. patent law, a form of patent infringement liability that occurs when multiple actors are involved in conveying out the claimed infringement of a method patent and no unmarried accused infringer has performed all of the steps of the method.
Divisional patent application [edit]
A type of patent application which contains matter from a previously-filed application. Also referred to simply as "divisional awarding".
Doctrine of equivalents [edit]
A legal dominion that allows a court to hold a party liable for patent infringement even though the infringing device or procedure does not fall within the literal telescopic of a patent merits, but nevertheless is equivalent to the claimed invention.
Double patenting [edit]
The protection of one single invention past two patents ordinarily owned by the aforementioned proprietor.
Druckexemplar [edit]
At the European Patent Office, the application documents serving as the ground for the publication of the granted patent.
E [edit]
Elected function [edit]
Under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), a national patent office of or acting for a Country elected past the applicant under Chapter 2 of the Percentage.[26] See besides "Chapter II" above.
Embodiment [edit]
In a patent or patent awarding, "a specific combination of features or a specific style of carrying out the invention, by contrast to a more abstruse definition of features which can be carried out in more than 1 way."[27]
Essential patent [edit]
A patent challenge an invention that is required to implement a given industry standard.
Evergreening [edit]
Diverse legal, business and technological strategies past which patentees extend or effort to extend the patent protection for their products.
Exhaustion of rights [edit]
A legal concept co-ordinate to which intellectual holding (IP) rights, such equally patent rights, in a product are exhausted by its sale. The concept of national exhaustion (exhaustion past sale in the domestic market), which is recognized in nearly countries around the world, is distinguished from the concept of regional or international exhaustion (exhaustion past sale in the domestic market place), which is recognized in some countries but not in others.[28]
Exam support certificate [edit]
According to USPTO patent rules, the examination support certificate (ESD) is a document submitted by an applicant that lists prior art and identifies how the prior art applies to the claims in a pending patent application.
F [edit]
Fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory licensing [edit]
A type of licensing typically used during standardisation processes. Likewise abbreviated "FRAND".
Field-of-use limitation [edit]
A provision in a patent license that limits the scope of what the patent owner authorizes a manufacturing licensee (that is, a licensee that manufactures a patented production or performs a patented procedure) to practice in relation to the patent, by specifying a defined field of permissible operation or specifying fields from which the licensee is excluded.
File wrapper [edit]
The special folder blazon holding a U.Southward. patent application. The "file wrapper" was a large three section binder that interlineated to close into one large "wrapper." These paper File wrappers were fully digitized every bit of June 3, 2003 and are now chosen Image File Wrappers (IFW).
Filing date [edit]
The filing date of a patent application is the engagement the patent application was filed in one or more patent offices, i.east. the appointment on which that awarding is legally accustomed at the patent role. That engagement is typically the date on which the documents are deposited at the part, simply may exist afterward if there are defects in the documents. Come across also Priority right.
In the Us, if a patent awarding is mailed to the Usa Patent and Trademark Function (USPTO) past Express Mail service, Mail Part to Leaseholder, and so the engagement the awarding was deposited in the post office is the filing date.[29]
First sale doctrine [edit]
See Exhaustion of rights.
First to file [edit]
A legal concept in which the right to a patent for an invention is adamant by the start person to file for a patent to protect that invention, cf. First to invent.
Outset to invent [edit]
A legal concept in which the right to a patent for an invention is determined by the first person to make that invention, cf. First to file.
Flash of genius [edit]
A examination for patentability formerly used by the United States Federal Courts.
Foreign filing license [edit]
An authorization granted past a governmental authority to an applicant to apply for a patent in a country outside its own state. Meet likewise Patent application#Security issues.
Freedom-to-operate [edit]
A freedom-to-operate search is a search aimed at establishing whether a product or procedure is covered past patent rights, including patent and patent applications. If it does, commercially exploiting the product or process may lead to patent infringement. Freedom-to-operate analyses and opinions are aimed at determining the risk of patent infringement in that respect. These searches and opinions are also called clearance searches and opinions.
Further medical use [edit]
See Second medical utilise.
One thousand [edit]
Gebrauchsmuster [edit]
A utility model in German and Austrian laws.
I [edit]
Contained claim [edit]
A claim that does not incorporate the features of any other claim.
Indirect infringement [edit]
When a patent is infringed by some party other than the one actually directly engaged in the infringement of the invention, but the original party is the crusade of the infringement. For case, when a third party supplies a product which is intended to be used, or can only be reasonably used or worked upon to make the device claimed in a patent. In some jurisdictions, forms of indirect infringements include "contributory infringement" and "induced infringement".
Induced infringement [edit]
A form of indirect infringement.
Industrial applicability [edit]
A requirement of many patent systems, requiring that an invention exist capable of industrial applicability in order for a patent to be granted for that invention.
Information disclosure statement [edit]
In Us patent law, a submission of relevant groundwork fine art or data to the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) past an applicant for a patent during patent prosecution.
Innovation patent [edit]
A type of patent in some countries used for inventions that have a short commercial life or that offers a comparatively small accelerate over existing technology. It often has a shorter term of protection, for example 8 years instead of 20 in Australia. See also utility model and little patent.
Interference proceeding [edit]
Under U.Due south. patent law, proceedings to make up one's mind who is entitled to the grant of a patent for an invention.
Intermediate generalisation [edit]
At the European Patent Part (EPO), an amendment to a claim resulting in "an undisclosed combination of selected features lying somewhere between an originally broad disclosure and a more express specific disclosure".[30] [31]
International application [edit]
A patent application filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT).[32] Too called "PCT awarding".
International phase [edit]
The period of fourth dimension from the filing of a Percent application to the entry into national phases.
International preliminary examination report (IPER) [edit]
An exam written report prepared under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT).
Invalidity opinion [edit]
An invalidity opinion, likewise chosen "validity opinion", is a legal opinion provided by an attorney on how a court might rule on the validity of an issued patent. Invalidity opinions are often sought prior to patent litigation. Run across Patent infringement.
Invention disclosure [edit]
A confidential certificate written by a scientist or engineer for use by a visitor's patent department, or by an external patent chaser, to make up one's mind whether patent protection should exist sought for the described invention.
Invention promotion firm [edit]
A firm providing services to inventors to help them develop or market their inventions.
Inventive step [edit]
A patentability requirement co-ordinate to which an invention should exist sufficiently inventive, i.e. non-obvious, in order to be patented.
Inventor [edit]
The actual devisor of an invention that is the subject field of a patent. The inventor's employer is non the inventor. More than 1 inventor can be named on a patent.
Inventor'south document [edit]
A form of recognition granted by communist states to inventors. "It does not grant to the inventor the exclusive right to apply the invention or to preclude others from doing so simply, rather, signifies that the invention is state property."[33] Run into also author's certificate.
K [edit]
Kind code [edit]
A code including a letter and often a digit, indicating a kind of patent document (due east.g., published application or granted patent).
Kokai [edit]
A published, unexamined Japanese patent awarding.
Kokoku [edit]
An examined and approved Japanese patent application.
L [edit]
Large entity [edit]
In United States patent law, 1 of the bachelor bidder's status, along with the "small entity" status and the "micro entity" condition.
Letters patent [edit]
An old term for a patent, sometimes used in reference to a bound formal re-create of a patent provided past the USPTO to the inventor upon a patent'south effect.
License [edit]
A contract wherein a party (the "licensor") grants to another party (the "licensee") the authorization to utilise an invention which is subject to a patent, generally in commutation of a financial compensation, the royalties.
M [edit]
Motorcar-or-transformation examination [edit]
A criterion in United States patent law, according to which a claimed process is patent-eligible (nether § 101) if: (1) it is tied to a detail machine or apparatus, or (2) it transforms a particular article into a different state or matter. See as well: in re Bilski.
Maintenance fee [edit]
A fee to be paid to maintain a patent or a patent awarding in force. As well called "annuity fee" or "renewal fee".
Markman hearing [edit]
A pre-trial hearing in the United States court arrangement during which a estimate hears testimony from both parties on the appropriate meanings of the relevant key words used in the claims of a patent, the infringement of which is alleged by the plaintiff.
Markush construction [edit]
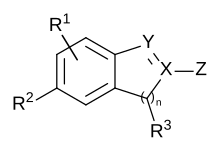
An example of a theoretical Markush construction.
A representation of a chemical structure covering a group of chemical compounds. Markush structures are commonly used in patent claims. A claim comprising a Markush structure is called "Markush claim".
McKesson Reference [edit]
In United States patent law, an Information Disclosure Argument (IDS) reference to a advice with a patenting authority (east.chiliad. office activeness response, or notice of allowance) in a related patent application. Based on the McKesson v. Span Medical[34] decision where inequitable carry was found where the bidder failed to notify the USPTO of such references. See as well Inequitable conduct.
Marlow Reference [edit]
In United States patent police, an IDS reference to a court document (e.g. memorandum stance, or a court order) pertaining to a litigation involving an application or a related patent/application. Based on the Marlow Industries, Inc. v. Igloo Products Corp.[35] decision where the court institute that the applicant had a duty to notify the USPTO of such references. See also Inequitable conduct.
Method [edit]
In United states of america patent constabulary, a patent may notably merits a process or method. The claim gives right to exclude operation of the procedure or method, regardless of the equipment or technology used to practice so.
Micro entity status [edit]
See "Pocket-sized entity status" beneath.
N [edit]
National phase [edit]
The prosecution phase wherein an international application filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (Per centum) becomes subject area to examination at a national level. In the United states, the term national stage is used instead—run into 35 U.S.C. § 371.
Non-obviousness [edit]
A patentability requirement co-ordinate to which an invention should not be obvious to a "person having ordinary skill in the art", in order to exist patented.
Not-patent literature [edit]
Any technical document that is neither a patent nor a patent application and that is submitted by a political party—such as an applicant, an opponent, or a third party—or cited by an examiner during patent prosecution. The non-patent literature includes particularly scientific papers used equally prior art to bear witness that an invention claimed in a patent or patent application was known or obvious before the filing of the awarding. Also abbreviated "NPL".
Non-provisional patent awarding [edit]
A U.s.a. patent application that is not a provisional awarding. The term arose in 1995 to distinguish what were at the time "normal" patent applications from the newly established provisional applications. A complete not-provisional application differs from a provisional in that a non-conditional must contain at least one claim and is to be examined. A non-provisional awarding may too merits priority to a prior filed application, which is not permitted with conditional applications.
Novelty [edit]
A patentability requirement according to which an invention is not patentable if it was already known before the date of filing.
Nullity activity [edit]
Lawsuit initiated by a political party requesting a patent to be declared invalid, i.e. to exist revoked. Also chosen "revocation action".
O [edit]
Objective technical problem [edit]
In the then-called "problem-solution arroyo" applied by the European Patent Office (EPO) to assess whether a claimed invention involves an inventive footstep (Commodity 56 EPC), the trouble that the notional skilled person is tasked with solving. If the skilled person, starting from the closest prior art and faced with the objective technical problem, would have arrived, without exercising any inventive skill, at the claimed invention, then the claimed invention is regarded as being obvious, i.due east. the claimed invention does not involve an inventive stride.
Role action [edit]
A formal written report from a Patent Office examiner to an inventor or attorney detailing which claims in a patent application were allowed for later on event (publication) in a patent and which claims were rejected. The examiner gives reasons for allowance or rejection.
On-sale bar [edit]
A concept of U.S. law in which the grant of a patent is prevented if the invention that is the subject field of the patent application was on sale more than i year prior to the priority date.
Opposition proceeding [edit]
Proceedings in which a 3rd party opposes the grant of a patent in an attempt to prevent that grant, or have the patent revoked. Opposition proceedings may exist pre- or post-grant.
P [edit]
Patent [edit]
A territorial right to foreclose others from commercially exploiting an invention, granted to an inventor or his successor in rights in commutation for the public disclosure of the invention. A patent is regarded as a specific type of intellectual belongings right, and is granted for a limited period of time, the term of the patent.
Patent ambush [edit]
A patent ambush occurs when a fellow member of a standard-setting organization withholds information, during participation in development and setting a standard, nigh a patent that the member or the fellow member's visitor owns, has pending, or intends to file, which is relevant to the standard, and afterward the company asserts that a patent is infringed past utilise of the standard as adopted.[36] [37]
Patent Awarding Locating and Monitoring Arrangement (PALM) [edit]
The Patent Awarding Locating and Monitoring Organization (PALM) is used to support the Reexamination process inside the USPTO. Reexamination is the test of a granted patent, which can result in the revocation of that patent. The PALM organization is used with both Image File Wrappers and paper File Wrappers. See Manual of Patent Examination and Procedure, Department 2235.
Patent caveat [edit]
Formerly, in U.s. patent law, a legal document filed with the United States Patent Office.[38] Caveats were discontinued in 1909. A caveat was like a patent awarding with a clarification of an invention and drawings, but without claims. It was an official find of intention to file a patent application at a later engagement.
Patent classification [edit]
Nomenclature of patents in technological areas for convenient retrieval during prior art searches.
Patent drawing [edit]
Technical drawing in a patent awarding, that illustrates the invention. It may be required by law to be in a particular form.
Patent family unit [edit]
A grouping of patents related by a common priority claim.
Patent flooding [edit]
Patenting every possible way of doing something.
Patent infringement [edit]
Commercially exploiting an invention claimed in a patent without permission of the patentee.
Patent misuse [edit]
In United States patent law, an affirmative defense used in patent litigation after the defendant has been found to have infringed a patent.
Patent model [edit]
A miniature model that shows how an invention works.
Patent monetization [edit]
The generation of revenue or the attempt to generate acquirement by a person or company past selling or licensing the patents it owns.
Patent awaiting [edit]

The plate of the Martin ejector seat of the armed services aircraft, stating "Patents pending in other dominions and strange countries". Dübendorf Museum of Military Aviation.
A warning that a patent application has been filed for an invention integrated in a product. The alarm indicates that the bidder(s) may be entitled to some rights even if a patent has non been granted however, or that the applicant(s) will be entitled to some rights once a patent is granted.
Patent pool [edit]
A consortium of at to the lowest degree two companies agreeing to cross-license patents and other IP rights relating to a item technology.
Patent portfolio [edit]
A collection of patents owned by a single entity, such equally an individual or corporation.
Patent specification [edit]
See specification.
Patent thicket [edit]
A dense web of overlapping intellectual belongings rights that a visitor must navigate through in club to commercialize new technology.[39]
Patent troll [edit]
A person or company who enforces patent rights against accused infringers in an attempt to collect licensing fees, but does non manufacture products or supply services based upon the patents in question. As well chosen a patent exclamation entity (PAE) or non practicing entity (NPE).
Patent picket [edit]
A process for monitoring newly issued patents on a periodic ground to see if any of these patents might exist of interest.
Patentability [edit]
A set of substantive requirements for a patent to be granted. An invention satisfying these requirements is said to exist patentable.
Patentability opinion [edit]
An opinion every bit to whether an invention might be patentable. Such an opinion may be established by a patent attorney to assist an inventor or company into deciding whether to file a patent awarding.[40]
Patentable subject matter [edit]
Patent systems exclude certain areas from the grant of patents. Cloth not so excluded is known as patentable subject matter.
Patentee [edit]
I to whom a patent was granted. As well called "patent holder", "patent proprietor", or "patent right holder".
Pay-for-delay [edit]
A deal nether which a company holding a patent on a drug pays a generic manufacturer to delay its launch of a cheap copy of the drug.[41]
PCT application [edit]
A patent awarding filed nether the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT). Also chosen "international awarding".
PCT Direct [edit]
A procedural scheme launched in 2014 past the European Patent Office (EPO). The scheme consists in allowing an applicant filing a PCT application claiming priority from an earlier application already searched by the EPO to reply –at the fourth dimension of filing the PCT awarding– to whatever objections raised in the search opinion fatigued up for the priority awarding.[42]
Person having ordinary skill in the art [edit]
A notional person having typical knowledge of a particular field or art, used such as to assess whether an invention is nonobvious or whether the specification of the patent enables i to practice what is claimed.
Petition to brand special [edit]
A United states of america patent law process that requests the U.Southward. Patent and Trademark Office to accelerate a patent's prosecution, based on a showing that certain conditions are met. For example, if the inventor is old or sick, or the field of invention is a favored surface area of science that significantly enriches people's lives, The U.S. PTO may allow such a petition.
Niggling patent [edit]
Phrase sometimes used to refer to utility models and Gebrauchsmuster, which are specific forms of patents for inventions normally granted for a shorter term, i.e. mostly 6 or 10 years instead of 20 years. In some jurisdictions, the patentability criteria applicable to petty patents are less stringent than those applicative to 20-year patents. See too innovation patent.
PHOSITA [edit]
In the United states of america, an abbreviation for "person having ordinary skill in the art".
Piracy [edit]
Pejorative term. Generally refers to the willful infringement of a patent. May besides be practical to the vigorous enforcement of a patent.
Pre-grant Publication [edit]
Pre-grant Publication (PGpub) is the procedure under 35 U.s.C. Section 122(b) requiring the publication of well-nigh U.s. patent applications eighteen months subsequently their filing dates.[43] This procedure was get-go enacted in the 1999 American Inventors Protection Act.
Preliminary injunction [edit]
An injunction issued by a courtroom prior to a final determination of the claim of a legal case, in society to restrain a party from going alee with a course of conduct or compelling a party to keep with a course of acquit until the instance has been decided. In patent law, a preliminary injunction typically allows a patent to exist enforced against an infringer prior to a concluding decision on the merits, i.east. while the infringement proceedings are awaiting. Depending on the jurisdiction, a number of requirements may have to be met for the court to grant a preliminary injunction, such as: urgency (to prevent imminent damage to the patentee'south concern), articulate infringement, and a sufficient likelihood that the patent is valid.
Prior art [edit]
Material publicly available prior to the priority engagement of an application which may anticipate the subject of and prevent the grant of a patent.
Priority right [edit]
A right to benefit from the filing date of an before application in a subsequent awarding. Challenge a priority right means that the filing engagement of the before application, i.east. the "priority appointment", rather than the actual appointment of filing of the subsequent application, volition be used equally the decisive date for assessing patentability of the invention claimed in the subsequent awarding.
Problem-solution approach [edit]
Nether the instance law and do of the European Patent Office (EPO), a systematic approach to assess whether an invention involves an inventive step. Also called "problem and solution approach".
Prosecution history estoppel [edit]
In certain states, most notably the United States, actions during prosecution can estop a party from sure later actions or assertions.
Provisional application [edit]
In United States patent constabulary, a legal certificate filed in the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) that establishes an early filing engagement, but which does not mature into an issued patent unless the applicant files a regular patent application within 1 yr. Run across likewise Non-provisional patent awarding.
Provisional (patent) rights or provisional protection [edit]
The rights conferred to a published patent application, i.eastward. the rights conferred before the patent is granted. Encounter also U.South. patent police force, 35 USC 154(d). Nether the European Patent Convention,
- "for the menstruum of conditional protection, between the moment of publication of the patent application and the moment of the publication of the patent grant, Commodity 67 EPC requires Member States to ensure that the applicant can claim bounty reasonable in the circumstances from any person who has used the invention in their territory. Following publication of the mention of the patent grant, full compensation of whatsoever losses suffered may be claimed, depending also on whether the infringer knew or should take known that he or she was infringing."[44]
R [edit]
Reading a claim [edit]
The process of establishing patent infringement involves "reading" a claim onto the engineering science of interest. If all of the merits's elements are found in the technology, the claim is said to "read on" the technology; if a single chemical element from the merits is missing from the technology, the claim does not literally read on the technology and the technology does not infringe the patent with respect to that claim. Also, the process of contesting or invalidating a patent tin involve showing that the claim reads on prior art, i.e., the claim's elements are found in the prior art.
Reasonable and non-discriminatory licensing [edit]
A blazon of licensing typically used during standardisation processes. Also abbreviated "RAND".
Reduction to practice [edit]
In United States patent police, making or performing an invention (actual reduction to exercise) or filing a patent application describing how to make and use an invention (constructive reduction to exercise). Of import for determining which party is "start to invent".
Reexamination [edit]
The exam of a granted patent, which tin can effect in the revocation of that patent.
Regional patent [edit]
A single patent covering a set of countries. As of 2012, the only true regional patent roofing more than ii countries appears to be the OAPI patent.[45] The European patent, the Eurasian patent, and the ARIPO patent each effectively lead, once granted, to a bundle of national patents for which at that place might be split up translation requirements (for example in the European Patent Convention), maintenance fees,[46] [ citation needed ] durations of protection (for example with ARIPO)[47] and separate jurisdiction exist (a patent invalidated in 1 country might still be valid in others). The unitary patent for Switzerland and Principality of liechtenstein can also be regarded as a regional patent with a truly unitary upshot. See also unitary patent.
Regional phase [edit]
The prosecution phase wherein an international application filed nether the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) becomes subject field to examination at a regional level. There are four regional patent treaties: the European Patent Convention, the Eurasian Patent Convention, the Bangui Agreement (see African Intellectual Belongings Organization or OAPI), and the Harare Protocol (run across African Regional Intellectual Property System or ARIPO). Meet as well National phase.
Registration patent [edit]
A type of patent that takes result, even if the substantial requirements (east.thousand. regarding novelty) accept non been fulfilled. The Belgian, Dutch and French patents are examples of registration patents.
Reissue patent [edit]
A U.S. patent that is reissued past the USPTO after the patentee filed an application for reissue, because the originally issued patent was regarded as lacking.[48]
Rejection [edit]
In the U.s.a., to have patent claims "rejected" in a patent awarding ways that the subject thing as claimed is considered by the patent examiner to exist unpatentable.[49] A terminal Part action based on rejection of claims is field of study to review by the Lath of Patent Appeals and Interferences (BPAI). cf Objections, supra.
Request for continued exam [edit]
In the United States, a request by an bidder for continued prosecution after the patent office has issued a "terminal" rejection or after prosecution "on the merits" has been closed (for example past a Notice of Allowance (NOA)).
Research exemption [edit]
In some legislations, an exemption to the rights conferred by patents, pursuant to which performing research and tests for preparing regulatory approval does not constitute infringement for a limited term before the end of patent term.
Restitutio in integrum [edit]
In the European Patent Convention, a means of redress following a loss of right due to the non-observance of a time limit in spite of all due care.
Revocation action [edit]
Lawsuit initiated by a party requesting a patent to be alleged invalid, i.e. to be revoked. Also chosen "nullity action".
Southward [edit]
Sandor Obviousness [edit]
In United States patent law, an obviousness rejection based on a single reference. Generally a case for an obviousness rejection requires the examiner to rely on 2 or more references. Sandor Obviousness stems from Ex Parte Sandor Nagy[50] where the examiner relied on only a single reference to reject the claims at issue. Ultimately the case was remanded on entreatment back to the examiner.
Search written report [edit]
A written report established by a patent office, which mentions documents which may exist taken into consideration in deciding whether the invention to which a patent awarding relates is patentable.
2d medical use [edit]
The patenting of a particular medical utilize of a molecule (or more than mostly production or composition), wherein a first detail utilise of a molecule is already known and, therefore, wherein the novel and inventive aspect lies solely in the 2nd use of the molecule. Likewise known as further medical utilize.
Selection invention [edit]
An invention consisting in the selection of private elements, sub-sets, or sub-ranges, within a larger, known prepare or range.[51] A selection patent is a patent granted on a selection invention.[52]
Pick patent [edit]
See selection invention.
Shop right [edit]
In U.Due south. patent constabulary, an implied license under which a firm may use a patented invention, invented by an employee who was working within the scope of their employment, using the firms' equipment, or inventing at the firms' expense.
Skilled person (in the fine art) [edit]
Encounter person having ordinary skill in the art.
Modest entity condition [edit]
In United States patent police force, a status allowing small businesses, independent inventors, and nonprofit organizations to file a patent application and maintain an issued patent for a reduced fee. An entity that does not qualify for modest entity status is charged double the fees charged pocket-size entities.[53] [54]
Changes to Usa patent law in December 2012 created a sub-category of Small Entity Status chosen "Micro Entity Status"[55] for inventors who qualify for Modest Entity Condition, but also have a gross income less than a certain corporeality, and accept assigned their patent(s) to their employer which is an institution of college teaching.[56]
Software patent [edit]
A patent in the field of computer software. Some types of inventions in the field of software are legally considered not-patentable field of study-matter, depending on the jurisdiction. See also software patents under the European Patent Convention, under TRIPs Understanding, under United Kingdom patent law, under United States patent law, estimator programs and the Patent Cooperation Treaty, software patent fence.
Specification [edit]
The specification, or patent specification, may either refer to the description of a patent or patent application, which is the meaning prevalent in the U.S.,[57] or to the complete patent equally granted, which is pregnant prevalent in Europe.[58]
Country of the art [edit]
A synonym for prior art.
Statutory Invention Registration [edit]
A procedure governed by MPEP Sections 1100 et al. in which a patent applicant could request a public filing of their awarding. Usually, this was used when the applicant felt a patent was no longer possible during the application period. It may now be obsolete due to the 1999 America Inventors Protection Act which required publication of U.Due south. applications in 18 months unless an exception applied.
Submarine patent [edit]
A patent first published and granted long after the original application was filed.
Sufficiency of disclosure [edit]
An important requirement to be met past a patent in society to be validly granted. Co-ordinate to this requirement, an invention must be described in the awarding or patent in a sufficiently clear and complete style to enable the person skilled in the art to carry out the invention.
Supplementary international search [edit]
A prior art search performed for an international (PCT) application in addition to the main international search provided for nether the Patent Cooperation Treaty (Percent).[59] The supplementary international search (SIS) is carried out by another International Searching Authority (ISA) than the ISA that carries out the main international search.[59]
Supplementary protection certificate [edit]
A sui generis right notably bachelor for medicinal and found protection products. The right comes into forcefulness afterward the corresponding patent expires and, for medicinal and plant protection products, has a maximum term (i.e., lifetime) of 5 years.
Swear dorsum of a reference [edit]
A process under U.S. patent law whereby an inventor can get a patent even if the invention has get public before the patent awarding was filed. Also "Swear behind a reference" or "Antedate" a reference. See 35 USC Department 102.
T [edit]
Technical character [edit]
A condition for an invention to be considered patentable under the example constabulary and practise of the European Patent Office (EPO). Namely, an invention must notably have a technical grapheme to be patentable. Run across for example Software patents under the European Patent Convention.
Term of patent [edit]
The maximum flow during which information technology can exist maintained in force.
Transfer [edit]
An operation past which ownership of a patent or patent application changes (for instance as a issue of a fiscal transaction).
Transitional phrase [edit]
In United states of america patent law, a phrase that links the preamble of a patent claim to the specific elements gear up forth in the merits which define what the invention itself really is. The transitional phrase acts every bit a limitation on the claim, indicating whether a similar device, method, or composition infringes the patent if it contains more or fewer elements than the claim in the patent.
U [edit]
Unitary patent [edit]
A patent having a unitary effect throughout the territories of more one country. The proposed unitary patent in the European Spousal relationship, as well called "European patent with unitary effect", is the about well-known unitary patent. Other unitary patents are the unitary patent in Switzerland and Principality of liechtenstein and the OAPI patent. Run into also regional patent.
Unity of invention [edit]
A requirement that a patent awarding can chronicle only to one invention (or to a grouping of inventions so linked as to form a single full general inventive concept, run into for instance Unity of invention under the European Patent Convention).
Utility [edit]
A patentability requirement mainly used to prevent the patenting of inoperative devices such equally perpetual motion machines.
Utility model [edit]
An intellectual property correct which is very similar to the patent, but commonly has a shorter term (oft half-dozen or 10 years) and may have less stringent patentability requirements. Encounter also lilliputian patent and innovation patent.
Utility patent [edit]
Phrase sometimes used, primarily in the United states, to distinguish the primary meaning of the term "patent" from other types of patents, such as design patents and plant patents. See besides: Patent#Definition.
5 [edit]
Validity opinion [edit]
A validity opinion, also called "invalidity opinion", is a legal opinion provided by an attorney on how a court might dominion on the validity of an issued patent. Validity opinions are often sought prior to patent litigation. Encounter Patent infringement.
X [edit]
X-Patent [edit]
Patent issued by the United states Patent and Trademark Office betwixt July 1790 (when the get-go U.S. patent was issued) and July 1836.
See as well [edit]
- List of patent case law
- Listing of people associated with patent police force
References [edit]
- ^ International Enclopedia of Comparative Law. BRILL. 1976. p. U-42.
A particular feature of the legal protection of inventions in the USSR is that legislation establishes two ways of protection: the author's certificate and the patent. The author of an invention may past his own selection require either only the recognition of his authorship or the recognition of his authorship and the grant to him of the exclusive right to the invention.
- ^ a b Ladas, Stephen Pericles (1975). Patents, trademarks, and related rights: national and international protection, Volume 1. Harvard University Press. p. 380. ISBN0-674-65775-6.
In the Soviet Union and in a number of Socialist countries, in that location is another kind of grant for an invention called Author'south or Inventor'south Document
- ^ EPO Board of Appeal decision T 1727/12 of 1 February 2016, point 1.2.
- ^ Bucknell, Duncan (2011). Pharmaceutical, Biotechnology and Chemical Inventions: World Protection and Exploitation. Oxford Academy Press. p. 274. ISBN9780199289011.
- ^ Section five(ane) of the German Utility Model Act
- ^ "Sun, EBay, Stone & Republic, Troyer: Intellectual Property". Bloomberg News . Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ^ Article 4(ane)(ii) PCT and Article 2(xiii) Percentage.
- ^ Article 31(four)(a) PCT and Article 2(xiv) PCT.
- ^ Guidelines for Exam in the EPO, section g-iv, 2 : "Enabling disclosure"; Guidelines for Examination in the EPO, section g-vi, 4 : "Enabling disclosure of a prior-art certificate"; Legal Research Service for the Boards of Appeal, European Patent Role, Example Law of the Boards of Appeal of the EPO (9th edition, July 2019), i.c.4.xi : "Reproducibility of the content of the disclosure".
- ^ Generics (UK) Ltd v Daiichi Pharmaceutical Co Ltd & Anor [2008] EWHC 2413 (Pat) (October fifteen, 2008), items 36–37.
- ^ Generics (UK) Ltd v Daiichi Pharmaceutical Co Ltd & Anor [2008] EWHC 2413 (Pat) (Oct fifteen, 2008), item 40.
- ^ EPO Lath of Appeal decision T 0412/09 of ix May 2012, point 2.1.3, referring to decision T 890/02, OJ EPO 2005, 497, bespeak two of the reasons. See also T 1727/14 of thirteen.12.2018, reasons 1.1:
- "Das allgemeine Fachwissen im Sinne des Patentrechts entspricht dem Wissen, das dem Fachmann aufgrund seiner Ausbildung und seiner Berufserfahrung zur Verfügung steht. Fachzeitschriften hingegen versuchen in der Regel, dem Fachmann neue, für seine Tätigkeit relevante Inhalte zu vermitteln, as well Dinge, dice in der Regel noch nicht Teil des allgemeinen Fachwissens geworden sind, und es möglicherweise auch nie sein werden." (English translation: "The common general cognition inside the meaning of patent law corresponds to the noesis available to the skilled person on the basis of his education and professional experience. In dissimilarity, specialist journals endeavour in full general to impart to the skilled person new contents relevant to his action, i.e. things that take not still go function of the common general noesis and may never be part thereof.")
- ^ Conclusion T 0412/09 of 9 May 2012, point ii.1.3, referring to "T 890/02, point 2, and "Case Law of the Boards of Appeal" EPO, sixth edition, 2010, chapter I, section C.ane.five and last paragraph of section C.iii.2.six" and "decisions T 151/05, points iii.4.i, four.1 and 4.3 of the reasons, and T 452/05, point 2.4.one, paragraph (b)(two)".
- ^ Mark A. Lemley, Kimberly A. Moore, Ending Abuse of Patent Continuations, Boalt Working Papers in Public Law (University of California, Berkeley), Year 2003, Paper 20
- ^ European Patent Office Enlarged Lath of Appeal opinion G iii/08 of May 12, 2010, Reasons x.four, 10.5, ten.6, 10.7.
- ^ Opinion G 3/08 (May 12, 2010), Reasons 10.six.
- ^ "WIPO Digital Access Service". Retrieved February v, 2021.
- ^ "EUIPO joins the WIPO Digital Admission Service (DAS)". Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ Lemley, Marking A., Rational Ignorance at the Patent Part (February 2001). Northwestern University Law Review, Vol. 95, No. four, 2001. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=261400 or doi:10.2139/ssrn.261400
- ^ Ruth Simon; Angus Loten (May 21, 2014). "States Revise Laws to Adjourn 'Patent Trolls'". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ^ Commodity 31 PCT
- ^ Run across for example Rule 43(4) EPC
- ^ Commodity ii(xiii) PCT
- ^ Determination Yard 2/10 of the Enlarged Board of Appeal of the European Patent Function, Baronial xxx, 2011, Reasons for the decision, point ii.1.
- ^ "... the term "disclaimer" is used in the decision as meaning an amendment to a claim resulting in the incorporation therein of a "negative" technical characteristic, typically excluding from a general feature specific embodiments or areas" in Determination Thousand 2/10, August 30, 2011, Reasons for the decision, betoken ii.2.
- ^ Commodity 2(xiv) PCT
- ^ Decision Thousand 2/10 of the Enlarged Board of Appeal of the European Patent Office, August 30, 2011, Reasons for the conclusion, point 2.3.
- ^ "International Exhaustion and Parallel Importation". WIPO. Archived from the original on August 12, 2012. Retrieved May 23, 2015.
- ^ USPTO § 1.10 Filing of correspondence past "Express Mail." – Appendix R Patent Rules Archived March 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ EPO Lath of Appeal decision T 1408/04 of 17 November 2006, reasons 1, third paragraph.
- ^ See also Guidelines for Test in the EPO, section h-five, 3.2.1 : "Intermediate generalisations", and Legal Research Service for the Boards of Appeal, European Patent Function, Case Police force of the Boards of Appeal of the EPO (9th edition, July 2019), ii.due east.i.9 : "Intermediate generalisations".
- ^ Article 2(vii) Per centum
- ^ "New Developments in Biotechnology:Patenting Life—Special Report (NTIS lodge #PB89-196612)" (PDF). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Function. April 1989. p. 162. Retrieved November 22, 2020.
- ^ McKesson v. Span Medical Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Marlow Industries, Inc. v. Igloo Products Corp., 2002 WL 485698 (N.D. Tex. 2002)
- ^ "Telecom standards face up patent ambush threat". ZDNet. June 15, 2005. Retrieved August 30, 2007.
- ^ "Antitrust: Commission confirms sending a Argument of Objections to Rambus". European Committee. August 23, 2007. Retrieved August thirty, 2007.
- ^ Patent Act of 1836
- ^ Carl Shapiro, Navigating the Patent Thicket: Cross Licenses, Patent Pools, and Standard-Setting, 2001, Innovation Policy and the Economic system (Vol. I) (Jaffe, Due east. et al., eds), pp. 119–150, MIT Printing.
- ^ Marker J. Thronson, Joel M. Grossman, Gabrielle S. Roth, Jon D. Grossman, Intellectual Belongings Legal Opinions (Loose Foliage), Aspen Publishers, 2008 Supplement, page ane-12. ISBN 978-0-7355-6194-6.
- ^ Something rotten, The Economist, August 6, 2009. Consulted on Baronial 7, 2009.
- ^ "Notice from the European Patent Office dated viii March 2017 apropos the processing by the EPO every bit International Searching Authority of informal comments on before search results ("PCT Direct")". Official Journal of the European Patent Office. European Patent Role (March 2017). March 31, 2017. Retrieved March 31, 2017.
- ^ "1120-". Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ^ European Commission, Pharmaceutical Sector Inquiry, Preliminary Report (DG Competition Staff Working Paper), November 28, 2008, page 98, footnote 116 (pdf, 1.95 MB). (Come across copyright detect in page 1: "Reproduction of parts of this report that are based on the Commission's own enquiry is authorised, provided that the source is acknowledged. For textile quoted in this report that is derived from other sources, permission must be sought directly from the copyright holder.")
- ^ James, Peter (November 3–6, 1999). "Regional Patent Systems in Africa". Open Forum Monte Carlo 1999. Monte Carlo: FICPI. Retrieved March three, 2012.
An manifestly unique feature of OAPI is that the OAPI patent is a single patent which extends to each member country.
- ^ "History of the Eurasian patent organization". Eurasian Patent System . Retrieved July two, 2012.
- ^ Peter James. "Regional patent systems in Africa".
- ^ MPEP § 1401 Reissue
- ^ "706-". Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ^ "Ex Parte NAGY et al - Page ane". Retrieved Apr 17, 2015.
- ^ Guidelines for Examination in the EPO, section g-vi, 8 : "Selection inventions" (Novelty), Guidelines for Test in the EPO, section chiliad-vii, 12 : "Selection inventions" (Inventive footstep).
- ^ Jochen East. Bühling, Dariusz Szleper, Thierry Calame, Nicolai Lindgreen, Nicola Dagg, Shoichi Okuyama,Working Guidelines, Question Q209, Selection Inventions – the Inventive Step Requirement, other Patentability Criteria and Scope of Protection [ permanent dead link ] , AIPPI. Consulted on March 29, 2009. "A selection patent is a patent granted for making an inventive selection from a field that is already known. Selection inventions may involve the selection of individual elements, sub-sets, or sub-ranges, which accept not been explicitly disclosed previously, within a larger known set or range."
- ^ 35 UsC. 41 (h)(1), 37 C.F.R. ane.27
- ^ "509-". Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ^ Federal Register, page 75033-75034, 37 CFR 1.29
- ^ Dec nineteen, 2012, Federal Register page 75034, left column
- ^ Come across for case MPEP 608 "...since each of these sections (specification, abstract, claims, sequence listings) of the disclosure are separately indexed..."
- ^ Run into for example Rule 73(1)(get-go sentence) EPC: "The specification of the European patent shall include the description, the claims and whatsoever drawings."
- ^ a b "CHAPTER 8: SUPPLEMENTARY INTERNATIONAL SEARCH". wipo.int. WIPO. Retrieved October 12, 2019.
External links [edit]
- Glossary at the Deutsches Patent- und Markenamt (DPMA), (German Patent and Trade Mark Office)
- Glossary at the European Patent Function (EPO)
- Glossary of patent terms at the The states Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO)
- PCT (Patent Cooperation Treaty) Glossary at the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- Article 2 PCT "Definitions"
- Glossary of patent related terms at the Trilateral Co-operation web site
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-Patent_Literature
0 Response to "European Patent Office Prior Art Nonpatent Literature Submission Date"
Post a Comment